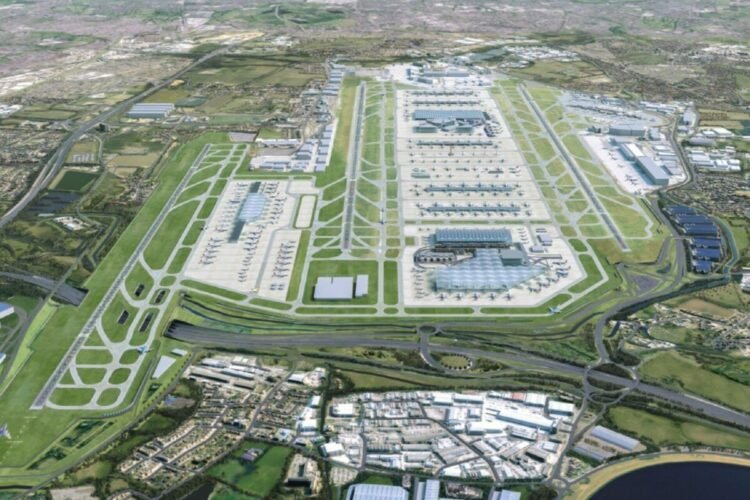
Heathrow Airport has submitted an ambitious and fully-funded proposal to build a third runway and expand its terminal infrastructure within the next decade, in a landmark move to re-establish the UK’s global aviation leadership and stimulate nationwide economic growth. The £49 billion project — 100% privately financed — is contingent on swift government action to implement policy changes and a regulatory framework that facilitates rapid execution.
With this proposal, Heathrow aims to unlock significant national benefits: up to 150 million passengers annually, 756,000 flights per year, at least 30 new destinations, and enhanced connectivity for UK regions. In return, the expansion promises to generate £200 billion in trade annually, increase the airport’s cargo capacity by 50%, and deliver a 0.43% boost to national GDP — with 60% of the economic benefit expected to be realised outside of London and the South East.
“It has never been more important or urgent to expand Heathrow,” said Heathrow CEO Thomas Woldbye. “With a green light from Government and the correct policy support underpinned by a fit-for-purpose regulatory model, we are ready to mobilise and start investing this year in our supply chain across the country.”
A Blueprint for National Growth
The centrepiece of the proposal is the construction of a new north-western runway measuring 3,500 metres — a design that has previously received Parliamentary backing. This would be complemented by:
- A brand-new terminal, T5X, adjacent to Terminal 5
- Three satellite terminals
- A significant expansion of Terminal 2
- Decommissioning and redevelopment of Terminal 3
- A redesign of the airfield to enable faster aircraft movement and reduce congestion
Of the total investment, £21 billion is allocated for the new runway and associated airfield works (up from £14 billion in 2018 due to inflation), £12 billion for new terminal and stand capacity, and £15 billion to modernise existing airport infrastructure.
According to Heathrow, much of the preparatory work — including stakeholder engagement, environmental assessments, and design — is already complete. If the Government responds by September 2025, the airport expects to begin public consultations in 2026, submit a planning application by 2028, and obtain planning permission by 2029.
Building a Greener, More Accessible Hub
Heathrow’s expansion proposal is underpinned by a commitment to sustainability and local inclusivity. The airport has reaffirmed its pledge to achieve net zero emissions by 2050 and highlighted measurable progress toward this goal. Since 2019, Heathrow has reduced carbon emissions from flights by approximately 10% and ground operations by 15%, while actively accelerating the adoption of Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF).
To mitigate environmental and community impacts, Heathrow has proposed:
- Enhanced rail services and new parkway stations
- Improved bus and coach connectivity
- A new road tunnel to streamline access
- Cycling and walking routes for staff and travellers
- A community fund to support local initiatives
- Stringent targets for air quality and noise management
The airport’s noise footprint has already shrunk by 41% since 2006, and all monitoring stations are within legal limits.
A Catalyst for Jobs and Regional Supply Chains
Tens of thousands of jobs are expected to be created through the design, construction, and operational phases of the expansion. Heathrow has committed to directing 60% of its supply chain expenditure to businesses outside of London and the South East — reinforcing its intention to deliver a truly national economic uplift.
Support from regional stakeholders has been robust. The Scottish Chambers of Commerce and Federation of Small Businesses Scotland praised the plan for strengthening connectivity to key markets. Cornwall Airport Newquay highlighted the potential for regional air links, provided access to slots remains affordable and consistent.
Meanwhile, industry leaders — including Kenton Jarvis, CEO of easyJet — see an expanded Heathrow as an opportunity to drive consumer value and competition. EasyJet, which has long aspired to operate at scale from Heathrow, welcomed the project as a path to offering lower fares to travellers.
Business and Industry Unify Behind Expansion
The third runway proposal has been endorsed by a broad coalition of UK business groups including the Confederation of British Industry (CBI), British Chambers of Commerce (BCC), MakeUK, the Institute of Directors (IoD), and the Federation of Small Businesses (FSB).
In a joint statement, the coalition said:
“The UK business community supports the expansion of Heathrow with a third runway — an investment in the nation’s future. It unlocks access to vital markets, drives private investment, and strengthens jobs and skills across the country.”
UK Steel also applauded the move, citing Heathrow’s pledge to prioritise British-made steel and its support of the UK Steel Charter as a strong signal of confidence in the domestic industry.
Urgency Amid Global Competition
The Heathrow Business Coalition warned that without expansion, the UK risks losing its competitive edge as a global aviation hub. While European counterparts continue to expand, Heathrow operates at full capacity, constraining trade, tourism, and connectivity. Currently, Heathrow connects UK exporters to 92% of the global economy via direct flights — a strategic asset at risk if growth is stalled.
Next Steps: Government Response Needed
To remain on schedule, Heathrow is requesting Government feedback by September 2025. Should the policy framework align, Heathrow is poised to launch national consultations in 2026 and proceed with its Development Consent Order (DCO) application in 2028.
The project, if approved, represents the most significant UK infrastructure investment in decades — one that could reshape British aviation, regional connectivity, and economic development for generations.
The total investment figure of £49 billion includes £21bn for runway and airfield infrastructure, £12bn for new terminals including T5X, and £15bn for modernising existing terminals. These figures include inflation adjustments and rounding. The DCO will cover the full scope of expansion, ensuring all regulatory approvals are consolidated under a single application process.